- Microsoft PC Manager is a free tool by Microsoft for Windows 10 and 11 that helps reduce high RAM usage safely and efficiently, offering a one-click "Boost" feature to quickly free up memory space and improve system performance.
- Modern apps and browsers consume a lot of RAM as they tend to run web-based processes. Microsoft PC Manager safely manages these processes with its "Boost" function, using system calls to free unused memory without affecting system stability.
- Besides manual boosts, the "Smart Boost" feature automatically optimizes RAM usage in the background, ensuring uninterrupted performance, and includes additional tools for process and startup app management to maintain optimal system health.
In the modern landscape of computing, Random Access Memory (RAM) is your system’s most contested resource. Whether you are a creative professional rendering video, a gamer seeking higher frame rates, or an office worker with dozens of browser tabs open, running out of memory inevitably leads to sluggish performance and system freezes.
For years, users relied on risky third-party “boosters” to solve this, but the era of questionable cleaner apps is over. Microsoft has released an official, native utility designed to handle system maintenance safely and efficiently: Microsoft PC Manager.
This guide explores how to utilize this powerful tool to instantly reduce RAM usage with a single click, automate your system’s health, and maintain a smooth Windows 11 experience without spending a dime on hardware upgrades.
The Modern Memory Dilemma
To appreciate why Microsoft PC Manager is such a vital tool, we must first understand why modern computers seem to devour RAM so voraciously.
Ten years ago, applications were relatively self-contained. Today, the software landscape has shifted toward web-based technologies. Your favorite chat apps (like Discord or Slack), your music player (Spotify), and even parts of the Windows interface rely on frameworks that essentially run a mini web browser for every application. Furthermore, modern browsers like Edge and Chrome isolate every single tab into its own “process” for security. While this prevents one crashing tab from taking down the whole browser, it means a simple browsing session can easily consume 4GB to 8GB of memory.
When your physical RAM reaches capacity—for example, hitting 15GB of usage on a 16GB system—Windows resorts to “paging.” This involves moving active data from your ultra-fast RAM chips to your much slower hard drive or SSD. The moment this transfer happens, your computer feels like it is moving through molasses.
Historically, fixing this required technical knowledge: opening Task Manager, identifying resource hogs, and nervously ending processes, hoping you didn’t just close a critical system file. Microsoft PC Manager eliminates this anxiety by providing a safe, automated “flush” mechanism that understands exactly what can be removed and what must stay.
What is Microsoft PC Manager?
Microsoft PC Manager is a desktop utility developed specifically to act as a safeguard and optimization hub for Windows 10 and 11. Unlike the bloated security suites of the early 2000s, this application is lightweight, follows the modern Windows design language, and integrates directly with the operating system’s native APIs.
It is not an antivirus replacement (though it integrates with Microsoft Defender), nor is it a registry cleaner. Instead, it aggregates several disparate maintenance tools—storage sense, startup management, and memory prioritization—into one simple, unified dashboard.
The Safety Advantage
The primary reason to choose this tool over third-party alternatives is safety. Because it is developed by Microsoft, the “Boost” function does not use “hacks” to free up memory. It uses legitimate system calls to trim the “working set” of applications and clear the “standby list” (cached memory that is no longer needed). This ensures that while your RAM usage drops, your system remains stable, and no active data is lost.
The “One-Click” Boost: How It Works
The flagship feature of Microsoft PC Manager is the “Boost” button. It is the first thing you see when you launch the app, and it is designed for instant gratification.
When you click this button, the application performs two distinct operations simultaneously:
- Memory Compression and Release: The tool signals to the Windows kernel that it should evaluate all running background processes. It identifies memory pages that have been allocated to apps but aren’t actively being used. It then compresses these pages or releases them back to the available pool. Additionally, it clears the standby cache—data that Windows keeps handy “just in case” but doesn’t strictly need.
- Temporary File Destruction: Simultaneously, it sweeps through the temporary folders used by Windows and your browsers. It deletes log files, error reporting fragments, and temporary internet files that clutter the drive.
The result is immediate. Users often report a reduction in memory usage ranging from 15% to 30% within seconds of clicking the button.
Step-by-Step: Installation and Setup | How Microsoft PC Manager Manages Memory on Windows 11
While Microsoft PC Manager is becoming standard in some regions, many users will need to install it manually. Here is how to get it up and running.
Phase 1: Downloading the Tool
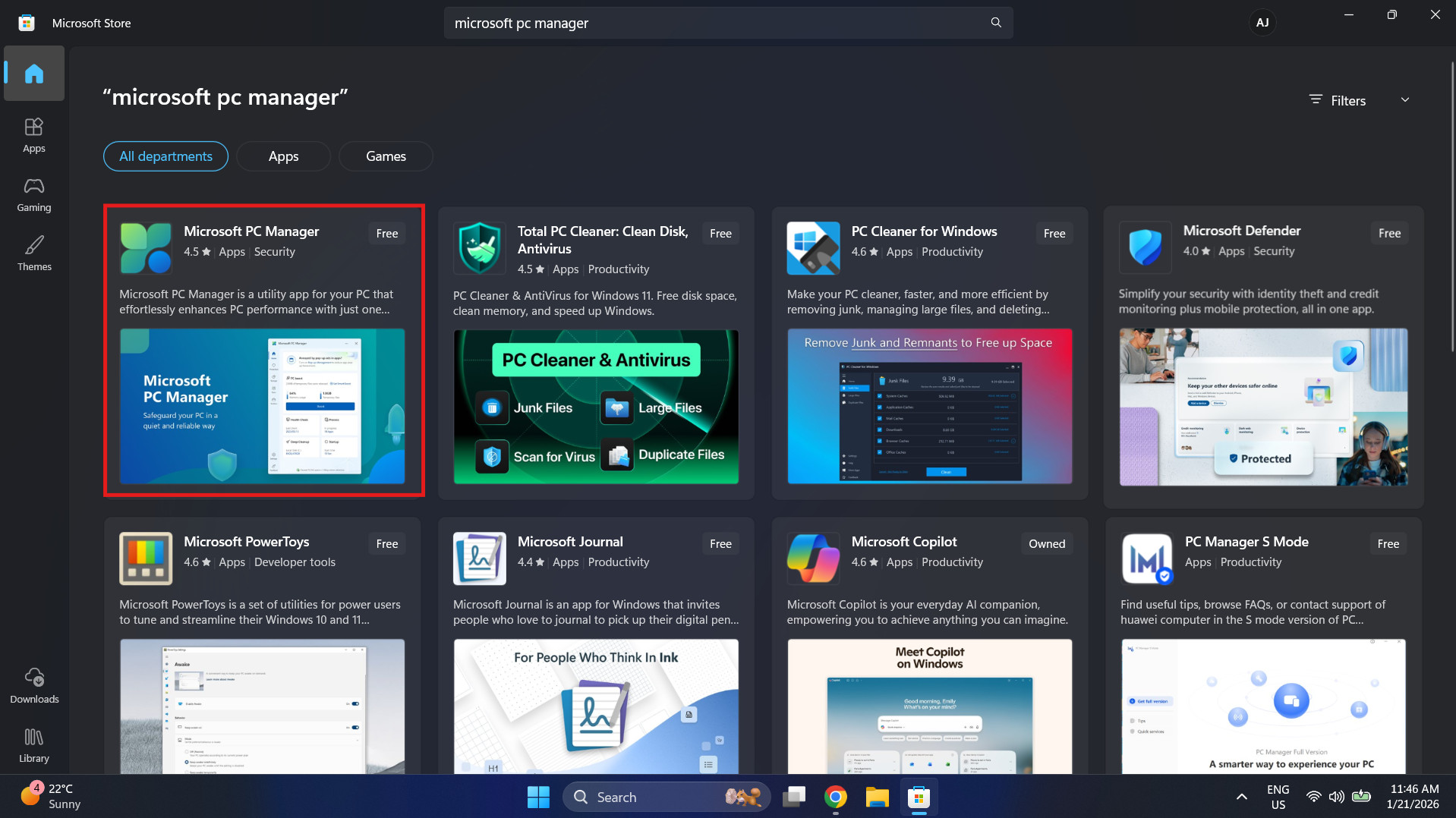
- Launch the Microsoft Store from your taskbar or Start menu.
- In the top search bar, type “Microsoft PC Manager”.
- Click on the Microsoft PC Manager app.
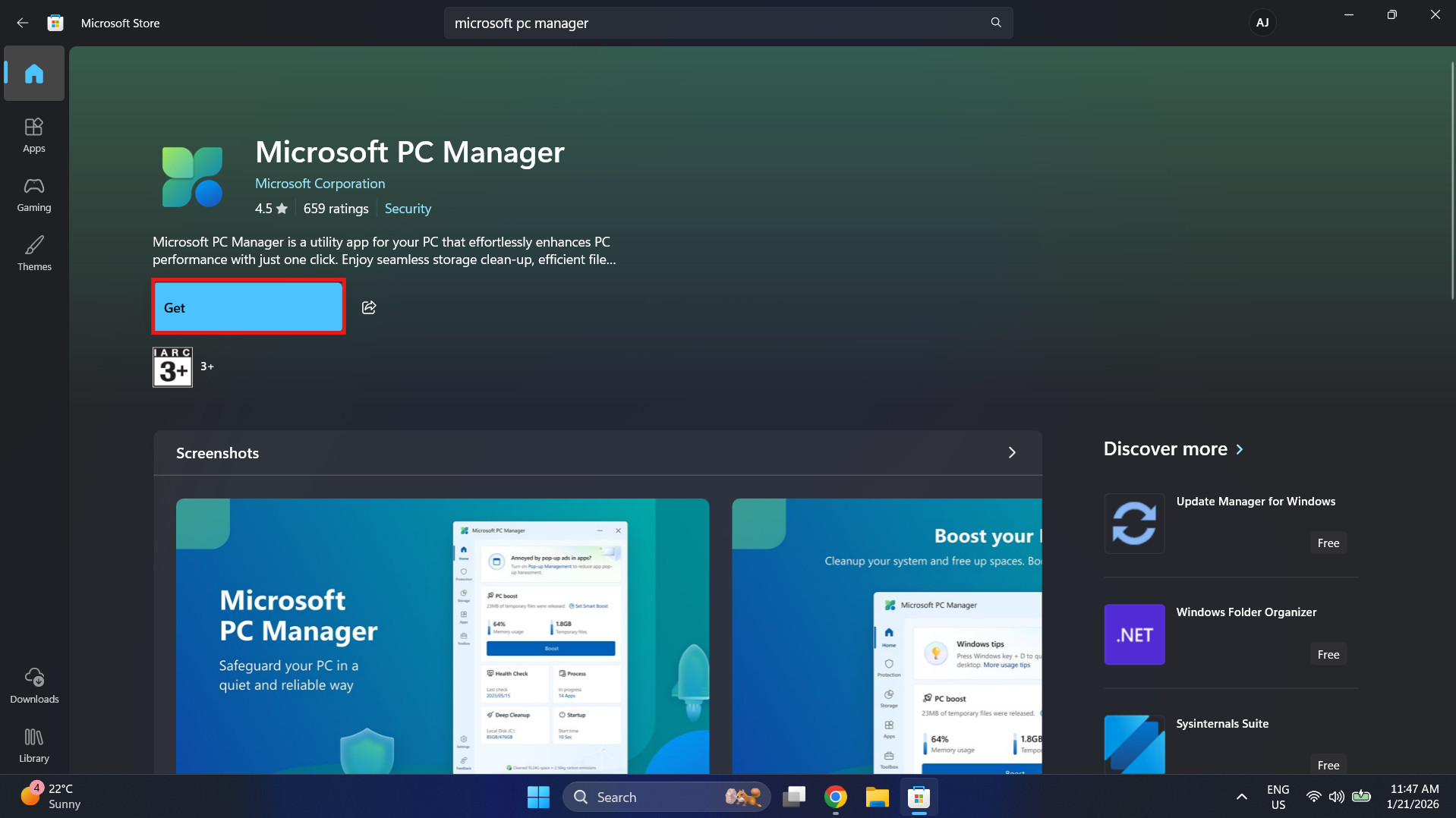
- Click the “Get” or “Install” button. The file is small and should download in moments.
- Once installed, click Open.
Phase 2: The Interface Tour
Upon launching, you will notice that the app behaves more like a sidebar widget than a full-window program. It docks neatly to the side of your screen.
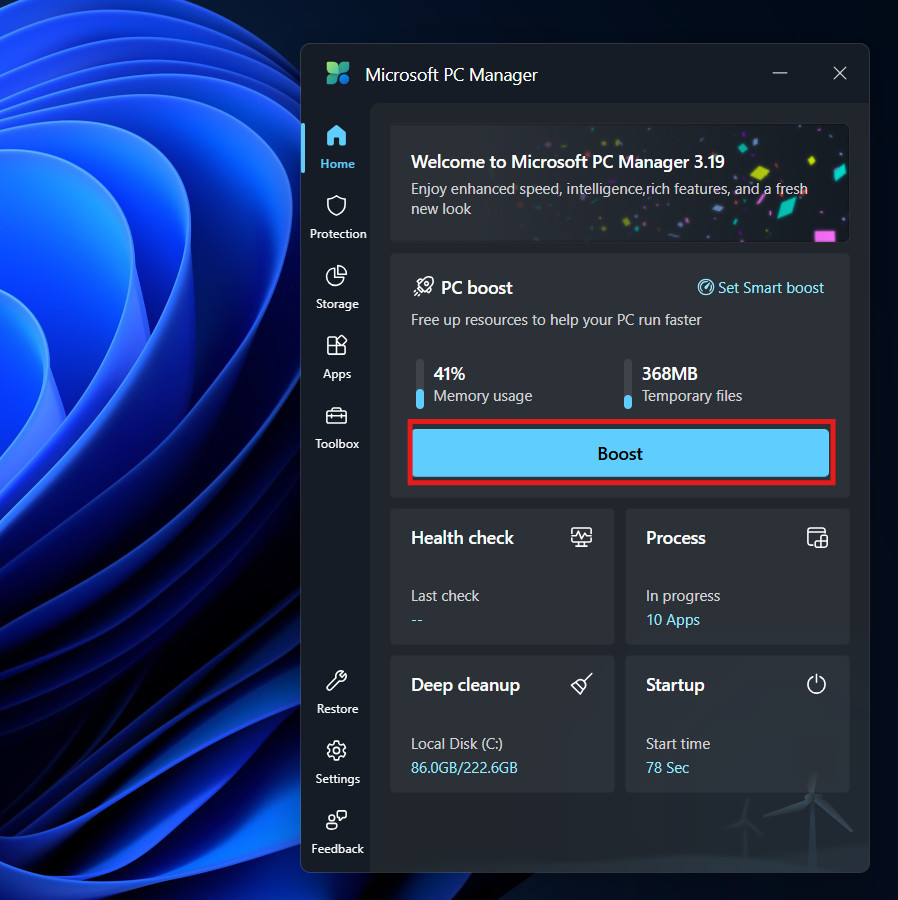
The “Home” tab presents a clear dashboard:
- Memory Usage: A large percentage indicator showing exactly how much of your RAM is currently occupied.
- Temporary Files: A real-time estimate of the junk data sitting on your drive.
- The Boost Button: A prominent blue button that triggers the optimization.
Phase 3: Executing the Boost
To reduce your RAM usage manually:
- Observe the memory percentage. If you have many apps open, it might read 80% or 90%.
- Click Boost.
- You will see a brief animation (usually a rocket ship or sweeping motion).
- Within seconds, the Temporary Files count will drop to zero, and the Memory Usage percentage will plummet.
If your system was lagging due to memory pressure, you should feel the responsiveness return almost instantly.
Automating Optimization with “Smart Boost”
While the manual button is satisfying to press, micromanaging your computer’s memory is tedious. You shouldn’t have to pause your work every hour to click a button. This is where the Smart Boost feature shines.
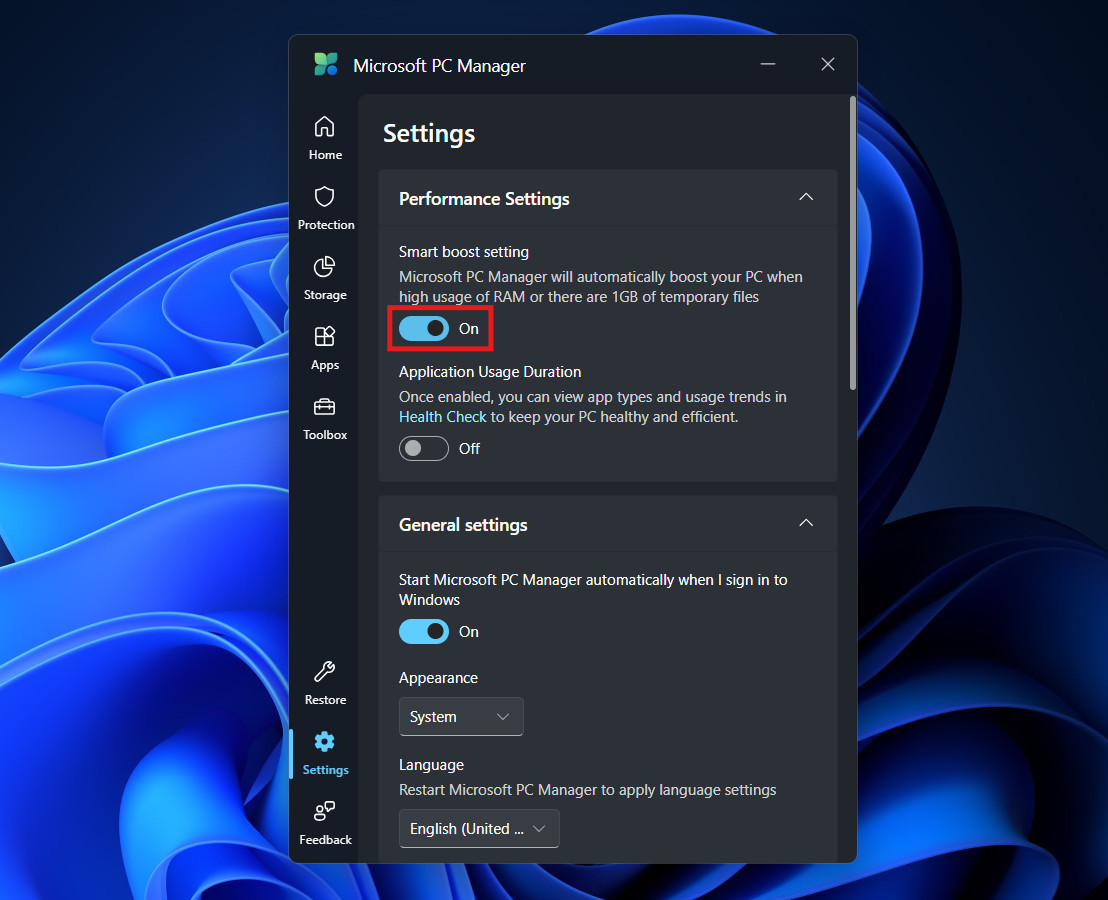
Smart Boost transforms Microsoft PC Manager from a passive tool into an active guardian. When enabled, it monitors your system resources in the background. If it detects that your RAM usage has spiked to critical levels (often highly utilized) or that temporary junk files have exceeded 1GB, it will silently run the optimization process without interrupting you.
How to Enable Smart Boost:
- Open the application.
- Click on the Settings gear icon (typically found at the bottom of the sidebar or in the top-right menu).
- Locate the section labeled “Smart Boost”.
- Toggle the switch to the On position.
With this active, your computer effectively “self-heals.” If you are deep in a gaming session or editing a massive video project, the tool will ensure that background processes don’t steal the RAM you need for your active task.
Going Deeper: Advanced Memory Management
High RAM usage is often just a symptom of a larger problem: too many unnecessary applications running simultaneously. While the Boost button treats the symptom, Microsoft PC Manager offers three other tools to cure the disease.
1. Process Management
This is a simplified, user-friendly version of the Windows Task Manager.
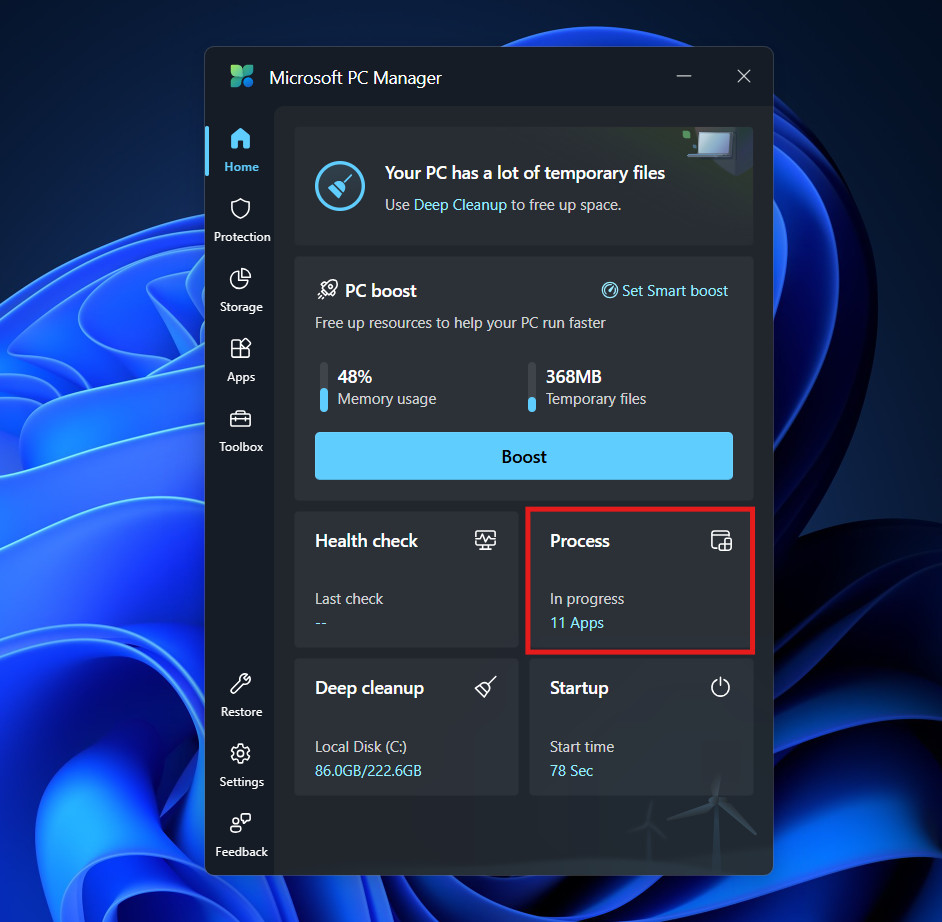
- From the home screen, select Process.
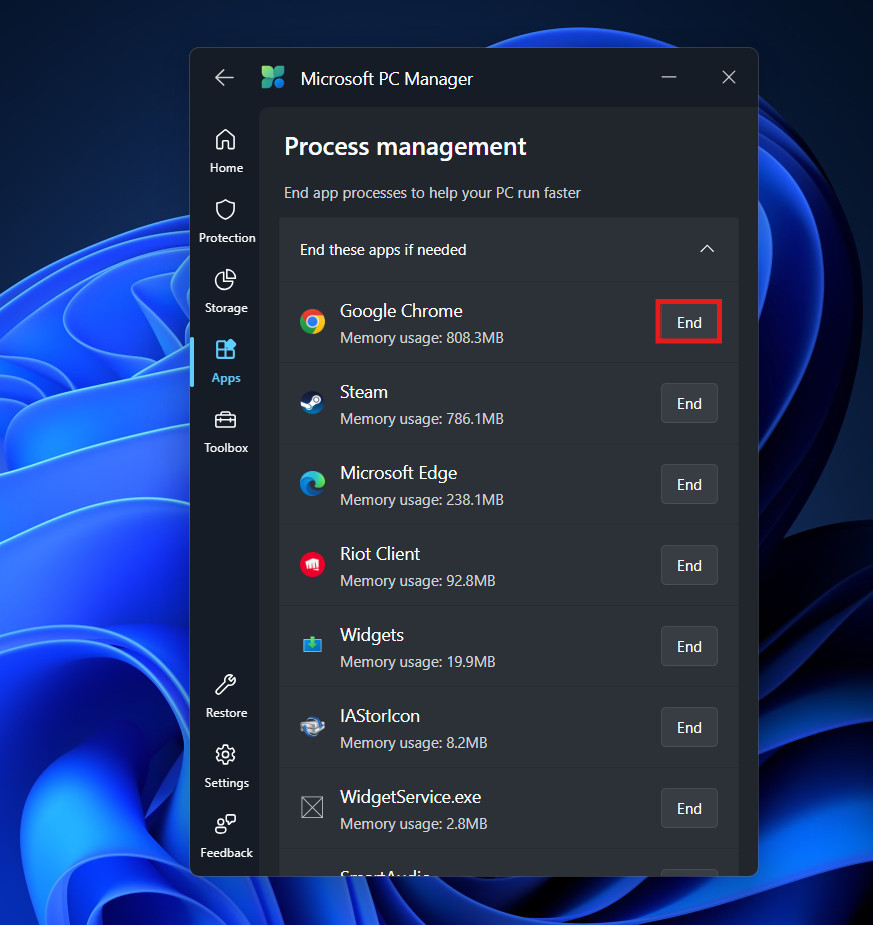
- The app presents a list of applications running in the background that are not currently being used.
- Next to each app, you will see exactly how much RAM it is consuming.
- If you spot a program you aren’t using (perhaps a game launcher you forgot to close), click the End button.
This completely terminates the application, reclaiming 100% of the resources it was holding. It is safer than the traditional Task Manager because it generally hides critical system processes that, if closed, would crash Windows.
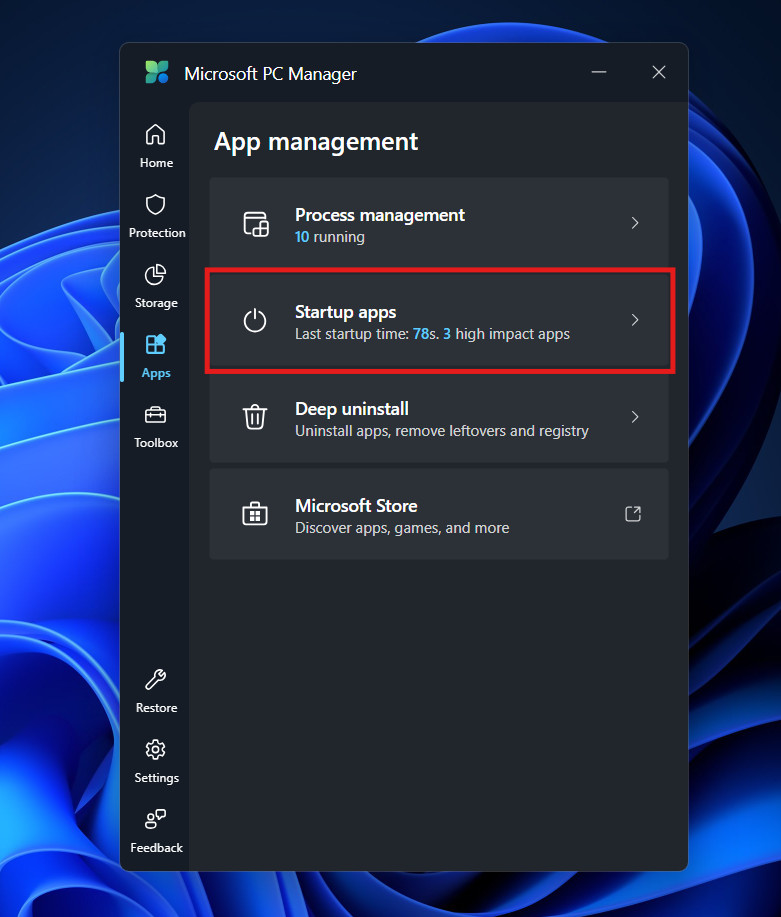
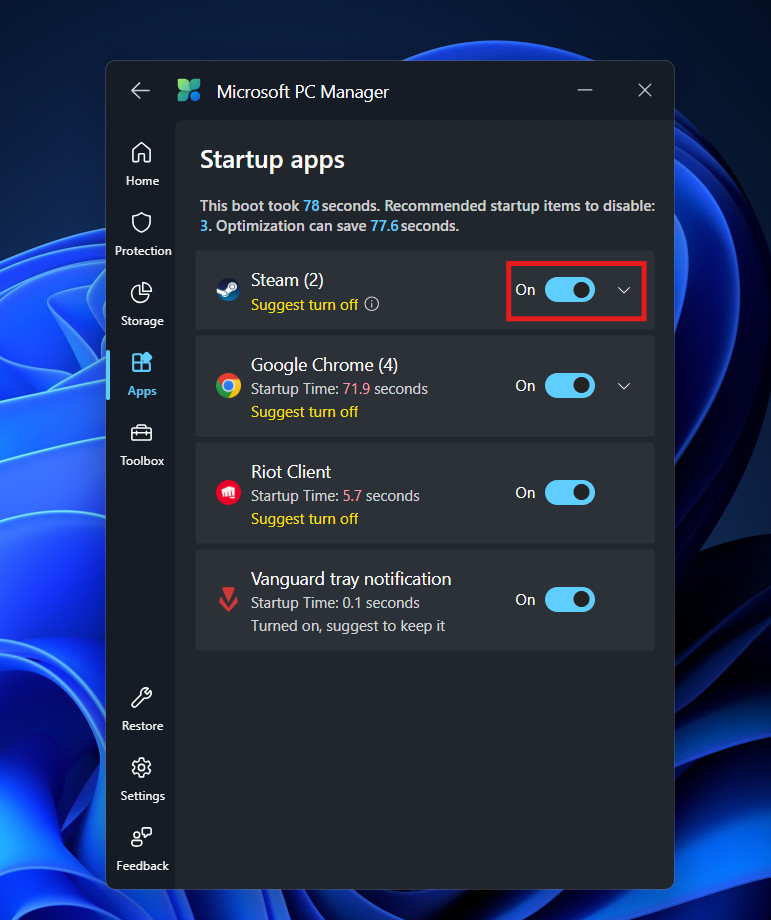
2. Startup App Management
The most effective way to reduce RAM usage is to prevent apps from loading when you turn on your computer.
- Navigate to the Apps section.
- Now, click on the Startup apps section.
- Review the list of programs set to launch at boot.
- You will likely find “high impact” offenders like music players, chat apps, or cloud sync tools that you don’t need immediately.
- Toggle them Off.
By disabling these, you lower your “baseline” memory usage. Instead of starting your day with 40% of your RAM already gone, you might start at 20%, giving you much more headroom for your actual work.
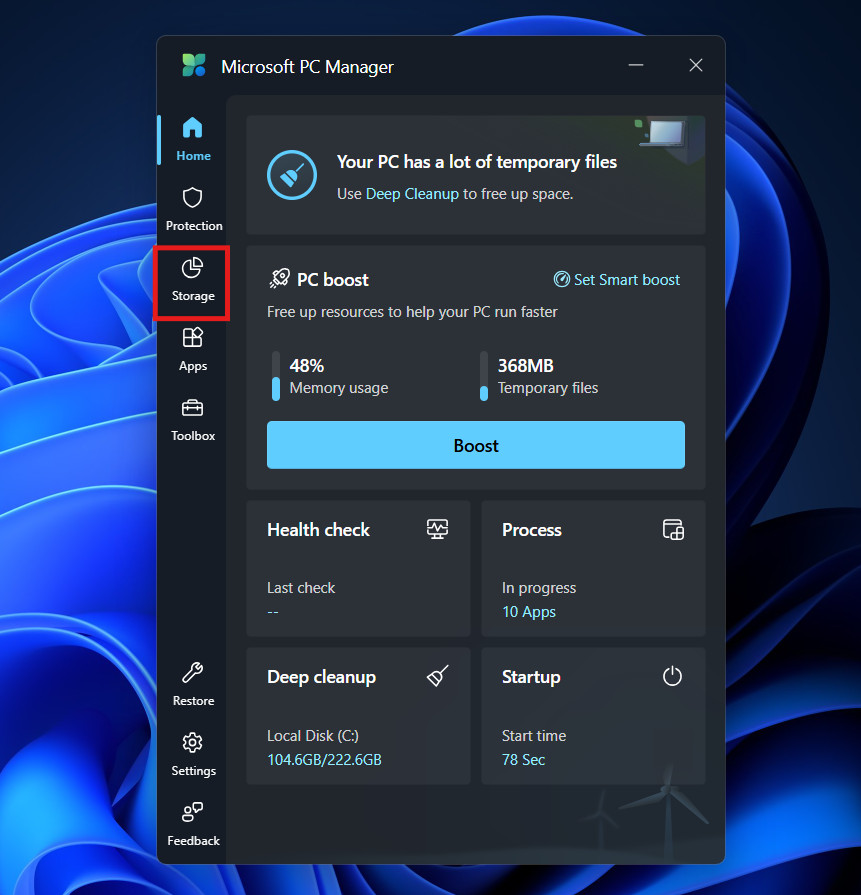
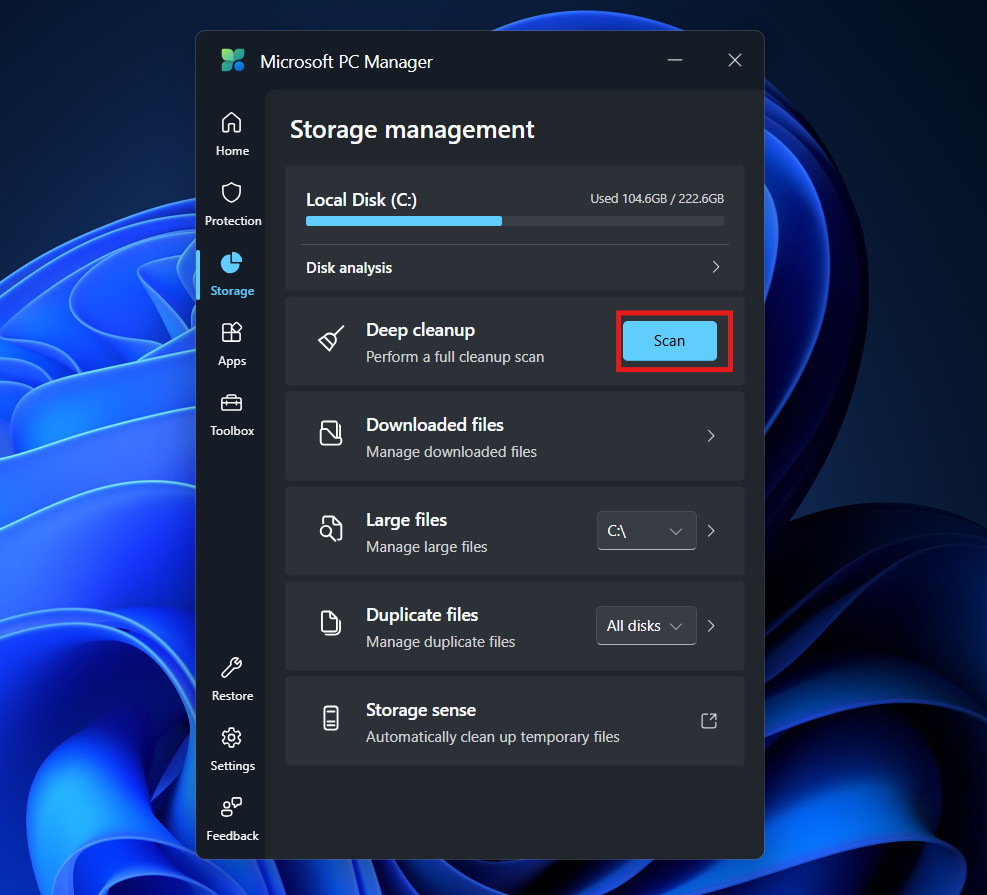
3. Deep Cleanup
While “Boost” handles basic temporary files, the Deep Cleanup feature digs into the system cache.
- Click on Storage.
- Under Deep cleanup, click on Scan.
- The tool scans for Windows Update cleanup files, DirectX shader caches, and extensive browser caches.
- While primarily a storage tool, clearing these caches can resolve memory leaks that occur when applications struggle to process corrupt temporary data.
When to Use the Boost Feature
There is a common misconception that you should keep your RAM empty at all times. This is false. Unused RAM is wasted potential. Windows intentionally keeps data in memory to help your frequently used apps launch faster.
However, there are specific scenarios where forcing a flush via Microsoft PC Manager is highly recommended:
- Before Gaming: If you are about to launch a resource-heavy game, clicking Boost clears the standby list. This minimizes the chance of “stuttering” caused by the system having to frantically free up memory while the game is trying to load assets.
- After Heavy Workflows: If you have just finished a session in Adobe Photoshop or closed fifty browser tabs, some “ghost” processes might linger. A quick Boost ensures the slate is wiped clean for your next task.
- The “Slow Down” Moment: We all know the feeling—you have been working for six hours, and the PC just feels tired. A Boost refreshes the active memory pool, often restoring that “fresh boot” snappiness.
Conclusion
Windows 11 is a robust and capable operating system, but the reality of modern software development means that memory management remains a challenge. We ask our computers to do more than ever before, often with the same amount of hardware resources.
Microsoft PC Manager represents a shift in how Microsoft approaches system maintenance. It acknowledges that users need a simple, transparent, and effective way to manage their system’s health without navigating complex control panels or risking stability with third-party hacks.
By integrating the one-click Boost feature into your daily routine, or better yet, allowing Smart Boost to handle it for you, you can ensure that your RAM is always prioritized for the task at hand. It is a free, official, and effortless way to breathe new life into your PC.
ALSO READ: