- You can open ports in Windows Firewall using GUI, PowerShell, or Command Prompt, each method suits different admin needs, from manual setups to automated scripting across multiple servers.
- Always verify opened ports are functional and secure by testing with tools like Test-NetConnection, telnet, and netstat, and limit access using IP scope and network profiles (Domain/Private/Public).
Managing network access securely is critical when configuring any Windows Server environment. Whether you’re hosting a web application, SQL Server, FTP service, or any other network-based service, you must open the necessary ports in the Windows Firewall to allow incoming traffic. Failing to do so can block functionality, cause service disruptions, or lead to inaccessible applications.
This guide explains how to open port in Windows Firewall using different methods like GUI, PowerShell, and command prompt, tailored for Windows Server 2016, 2019, and 2022. If you’re wondering how to enable port in Windows securely, this tutorial gives you exact steps, security tips, and advanced configurations for administrators.
What Is a Port?
A port is a logical access point used by networking protocols to distinguish different services on the same device. For example, HTTP uses port 80, HTTPS uses 443, and RDP uses 3389.
Role of Windows Firewall
Windows Firewall acts as a built-in security layer that controls both inbound and outbound traffic based on rules. By default, it blocks most unsolicited inbound traffic to protect the system. If a service listens on a port, the firewall must be told to allow it.
Common Scenarios That Require Opening a Port
- Hosting a website using IIS (Port 80/443)
- Enabling Remote Desktop Protocol (Port 3389)
- Running SQL Server (Port 1433)
- Configuring FTP or SFTP (Port 21 or 22)
- Allowing custom application ports (e.g., 8080, 5000, etc.)
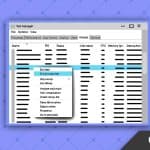
How to Open a Port in Windows Firewall (GUI Method)
If you’re running Windows Server 2016, 2019, or 2022 and need to open a specific port (for example, for a web server, database, or remote tool), follow these steps carefully:
Step 1: Open Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security
- Press
Windows + Rto open the Run dialog. - Type
wf.mscand press Enter. This will directly open the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security console.
Alternatively:
- Go to Control Panel → System and Security → Windows Defender Firewall.
- On the left panel, click Advanced settings.
Step 2: Open Inbound Rules
- In the left-hand navigation, click on Inbound Rules.
- These rules control incoming traffic to your server.
Step 3: Start a New Rule
- In the right-hand “Actions” pane, click New Rule.
- This opens the New Inbound Rule Wizard.
Step 4: Select Rule Type
- Choose Port (since you’re opening a port, not a program or protocol).
- Click Next.
Step 5: Choose Protocol and Port Number
- Select either TCP or UDP based on the requirement of your application or service.
- Choose Specific local ports and enter the port number you want to open (e.g.,
80,443,8080, etc.). - Click Next.
Step 6: Choose Action
- Select Allow the connection to permit traffic on the specified port.
- Click Next.
Step 7: Select Profile(s)
Choose when this rule should apply:
- Domain (for domain-connected environments),
- Private (for trusted networks),
- Public (for open/public networks).
Tip: For servers in a controlled environment, choose Domain and Private only.
Click Next.
Step 8: Name and Finish
- Give the rule a clear name like “Allow Port 8080 TCP”.
- Optionally, add a description for future reference.
- Click Finish.
Step 9: Confirm
- Your new rule should now be visible in the Inbound Rules list.
- Make sure it’s enabled and set to Allow.
How to Enable Port in Windows Server Using PowerShell
PowerShell is the most efficient way to configure firewall rules on Windows Server, especially when you’re managing multiple machines or want to automate tasks via scripts.
Basic Syntax
Use the New-NetFirewallRule cmdlet to create a new rule.
Example 1: Open TCP Port 8080
Example 2: Open UDP Port 161
Example 3: Allow a Range of Ports
Example 4: Remove a Rule
If you need to delete a rule: Remove-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName “Allow TCP Port 8080”
Pro Tip: Always test port access using Test-NetConnection after enabling it.
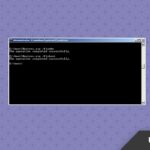
How to Open Port in Windows Firewall Using Command Prompt
The netsh command-line tool offers another way to open firewall ports. While not as modern as PowerShell, it’s still powerful and compatible with older Windows Server versions.
Example: Open TCP Port 8080
Example: Open UDP Port 69
Example: Delete a Rule
View All Rules (Optional)
This method is useful for batch files or remote sessions where PowerShell may be restricted.
Verifying That the Port is Open
After creating a rule, always verify that the port is reachable and not being blocked by another firewall or network restriction.
Method 1: Using PowerShell
If the TcpTestSucceeded result is True, the port is open.
Method 2: Using Telnet
-
First, install Telnet if not already available:
-
Then test:
Method 3: External Online Tools
You can use web-based port scanners (like canyouseeme.org) to test publicly accessible ports from outside your network.
Method 4: Netstat to Confirm Listening
Check if the port shows as LISTENING.
Advanced Firewall Configuration Tips
Here are some techniques to further secure and optimize your Windows Firewall configuration:
1. Enable Logging for Dropped Packets
Logging helps diagnose why traffic is being blocked:
- Open
Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security. - Click Properties (top-right pane).
- Go to Logging tab and enable logging for dropped packets.
2. Restrict by Remote IP
Limit which external IPs can connect to your open port:
- In your firewall rule, edit Scope.
- Under Remote IP Address, choose These IP addresses and add only trusted IPs.
3. Group Policy for Central Management
If you’re in a domain environment, you can push firewall rules using Group Policy:
- Go to Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).
- Create or edit a GPO:
Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Defender Firewall.
4. Use of Port Ranges for Services
Instead of defining many single-port rules:
5. Audit Firewall Events
Enable logging via Event Viewer:
- Navigate to:
Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Firewall With Advanced Security. - Enable operational log for detailed diagnostics.
Security Considerations When You Open Ports
- Do not open ports unnecessarily.
- Use only required profiles (Domain/Private/Public).
- Always pair port openings with service-level authentication or encryption.
- Monitor with event logs or intrusion detection.
When you enable ports in Windows, you also increase attack surface. Use minimal rules, audit regularly, and prefer VPN tunnels or proxies where possible.
FAQs
How do I open a port for SQL Server on Windows Server?
Use TCP port 1433. Open it using GUI or PowerShell as described above. Always restrict by IP if used in production.
How do I open ports in Windows Server 2022 specifically?
The steps are the same as for Server 2016/2019. Use Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security or PowerShell.
Can I open multiple ports at once?
Yes. PowerShell allows comma-separated values or port ranges:
LocalPort 8080,8081,8082
How to check if a port is open from outside the server?
Use telnet, online port scanners, or test-netconnection from a remote system.
What’s the difference between inbound and outbound rules?
Inbound rules allow incoming traffic to the server. Outbound rules manage traffic going out. For hosting services, you mainly configure inbound rules.
Conclusion
Opening a port in Windows Firewall on Windows Server is a fundamental but critical administrative task. Whether you’re setting up a web server, remote desktop access, or a custom application, knowing how to open port in Windows securely ensures smooth functionality and protected access.
Use the GUI for simplicity, PowerShell for automation, or command prompt for legacy compatibility. Always pair port openings with strong access controls and monitoring.
With the right configuration, you can confidently enable ports in Windows and maintain both performance and security across your server infrastructure.
ALSO READ:
- How to Resolve SSH Dispatch Run Fatal Errors on macOS Sequoia Firewall
- How to Allow Chrome To Access The Network In Your Firewall
- How to Disable Firewall in Windows 11
- How to Fix Command Prompt Not Working On Windows 11
- Alexa Not Working or Responding? Fix Echo Dot and Voice Command Issues
- Fix “Your Computer or Network May Be Sending Automated Queries” Error